Greetings Earthlings! 🙂
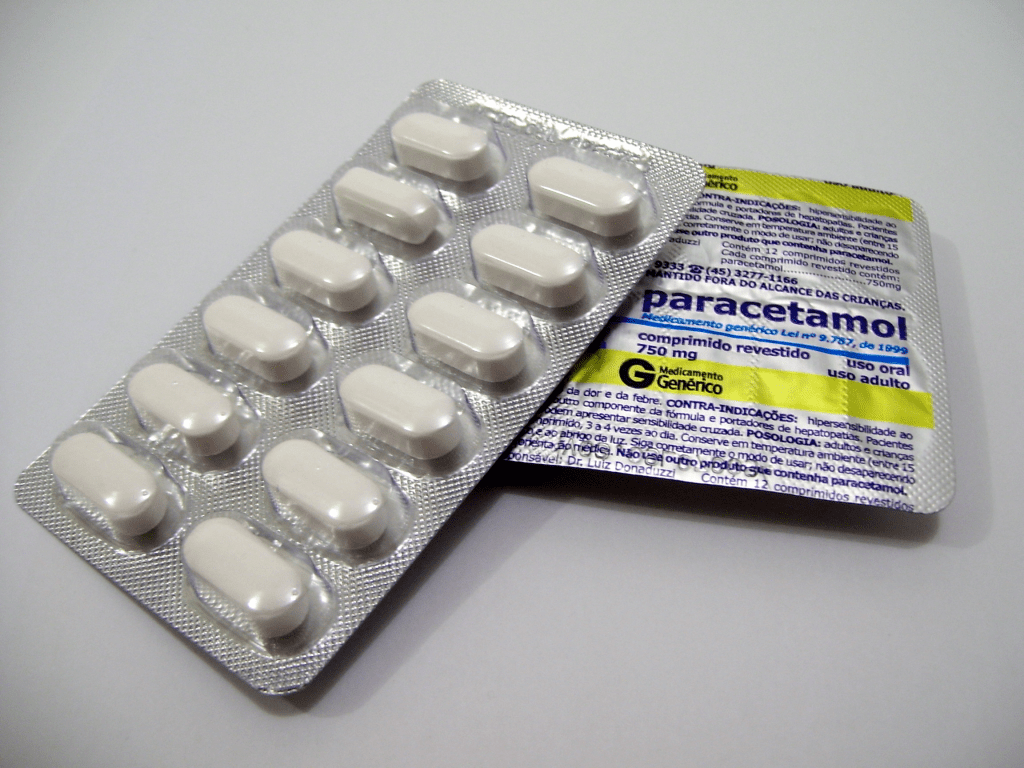
It is with my face cupped in my hands that I write this post for you after the latest “recommendations” coming from the States in recent weeks. In case you’ve been living under a rock, US president Donald Trump and RFK Jr., announced that there is a link between the use of paracetamol (also known as Tylenol) during pregnancy and the development of autism 🤦🏻♀️Historically this has been the safest drug that a woman can take during pregnancy to treat pain and fever (from infection), but now the Trump administration is slapping a warning label on this essential medication to scare women about the risk of autism when they’re at their most vulnerable.
So let’s separate fact from fiction- what does the research actually say?
Experts and researchers across the world have come out against these recommendations as the evidence largely does not support a causal link between autism and paracetamol. With regard to the current literature, there are often conflicting results in studies as it’s very hard to pin down accurate usage rates from medical records alone as paracetamol is an over the counter drug. Moreover, as it’s often used to treat other conditions, it’s hard to determine if any increase in autism rates is linked to the drug or the condition that paracetamol was used to treat. One of the largest studies of this type examined data from 2.5 million Swedish children from 1995-2019 to see if rates of paracetamol usage aligned with autism diagnoses. This study found that there was an increased likelihood, buuutttt not by much- 1.42% of children exposed to paracetamol were autistic versus 1.33% in those who were not exposed. I don’t think a 0.09% increased risk of autism is anything to write home about!

Sibling studies were also conducted to compare pregnancies where paracetamol had been given for one but not the other. These were performed as siblings are raised in the same environment, share genetic traits, and the health of the mother would have been similar for both pregnancies, removing a lot of factors that can influence the development of autism. This makes it easier to tell if paracetamol is having an impact in pregnancy. No links were found between the drug and autism in these studies.
On another note, researchers are of the opinion that the latest review of the research being pushed by the Trump administration hasn’t used the most robust of research methods. A more rigorous review of higher quality research was published on this topic earlier this year, and again, found no clinically significant risk of developing autism after paracetamol exposure in utero. The conflicting results seem to indicate a motivated agenda- and we all know how well that worked out last time with vaccines…

Research aside, telling a pregnant woman to “tough it out” instead of taking paracetamol is simply not good enough. High fever in pregnancy can be extremely dangerous, increasing the risk of complications like miscarriage, preterm birth, or neural tube defects (congenital malformations of the brain and spine such as spina bifida and Anencephaly- a fatal brain defect where parts of the brain don’t fully develop). If doctors are discouraged from administering this vital medication, the outcomes could be so much worse for the baby than autism. It beggars belief that Trump essentially deems the risk of autism to be worse than death. Even more so given that most experts agree that the American president himself is on the spectrum!
The important thing to remember about the research is that this link, however miniscule, is just an association. Just because it’s associated with autism, does not make it the cause. My mother, and thousands of others on social media, never took paracetamol during pregnancy, but all of them have children on the spectrum. If you’re an expectant mother, don’t let Trump scare you into avoiding paracetamol if you require it. Listen to your care provider and make the best decision for your health and your baby’s.
Hope you enjoyed this post dear Earthlings!
Have a lovely weekend! 🙂
Aoife























 Whilst I can’t recite the entire works of JK Rowling word for word, my brain does however, tend to randomly churn out eidetic memories every now and again (known as sporadic eidetic memory). I sporadically come out with full eidetic memories recalling such minuscule details as clothes, smells, songs, haircuts etc. My memories are so detailed that I once when recounting the previous night’s episode of Desperate Housewives to my Physical Therapist went so far as to mention the likely flavour of smoothie that the ladies of Wisteria Lane were drinking as they gossiped! 😂😬
Whilst I can’t recite the entire works of JK Rowling word for word, my brain does however, tend to randomly churn out eidetic memories every now and again (known as sporadic eidetic memory). I sporadically come out with full eidetic memories recalling such minuscule details as clothes, smells, songs, haircuts etc. My memories are so detailed that I once when recounting the previous night’s episode of Desperate Housewives to my Physical Therapist went so far as to mention the likely flavour of smoothie that the ladies of Wisteria Lane were drinking as they gossiped! 😂😬