Greetings Earthlings! 🙂
Following on from my post about autism and driving, this week I’d like to talk about autism friendly parking facilities!
So I was recently out looking for parking in my local shopping centre and was surprised to see a sign for ‘Autism Friendly Parking’ with designated spaces for autistic drivers/autistic passengers. Parking is perhaps, in my experience, one of the most stressful aspects of driving on the spectrum. The stress of trying to find a space, efforts to get into available spaces, the panic from holding up traffic when it takes you an age to get into an awkward spot- I would love to see what my blood pressure readings are like after it sometime!🙈 In all my years of driving I have never come across an autism friendly parking system, so naturally I had to investigate.
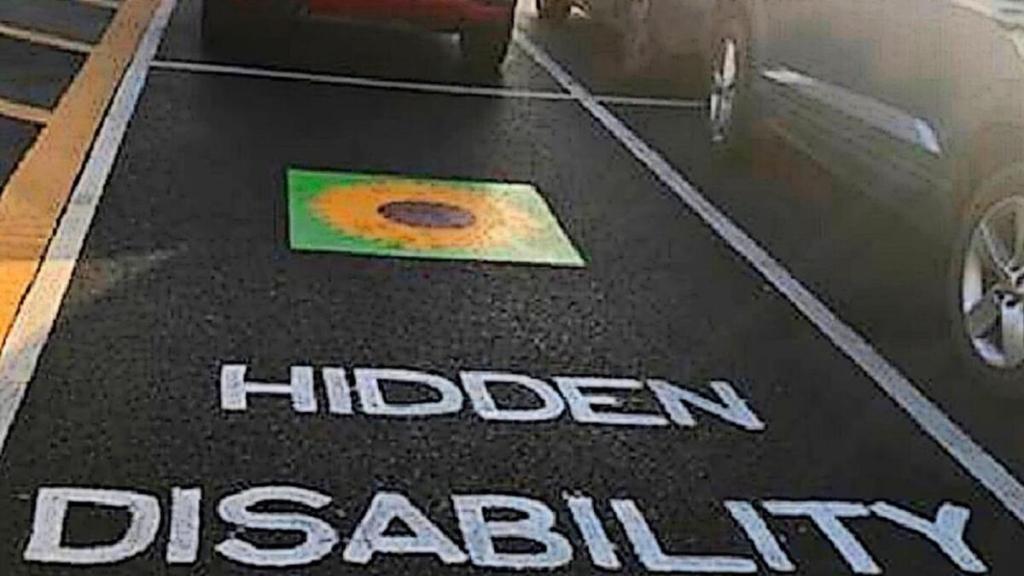





Many businesses have now started providing designated autism friendly parking. These spaces are located closer to the door of business’s (just like disabled sparking spots), to make life easier for autists, especially for those with mobility issues.
So in Ireland, you can apply to get an autism friendly parking permit. With proof of diagnosis and a small fee, you will be sent a permit to put in your car window which will allow you to avail of autism friendly parking spaces. These permits prevent abuse of the system and allow you to park in these spaces without fear of clamping. The permit also has the dual function of alerting emergency services that there may be an autistic driver/passenger in the car in the event of an accident, just like autism ID cards. So far this system is mainly provided by private businesses, but autism friendly towns like Dungarvan have implemented these parking schemes throughout the area. In recent weeks, Cork councilors are seeking to roll out a similar model to Dungarvan across the county, so this scheme could soon be a lot more readily available.
Similar schemes exist in other countries like the United States and the UK. In the UK for example, hidden disabilities like autism are now eligible for the blue badge scheme- the UK’s disability parking scheme, which enables autists to park in designated disabled parking spaces.

So if you find parking as stressful as I do, it’s worth investigating if there is an autism friendly parking scheme available in your area 🙂
Hope you enjoyed this post dear Earthlings!
Have a lovely weekend!
Aoife